 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Abstract
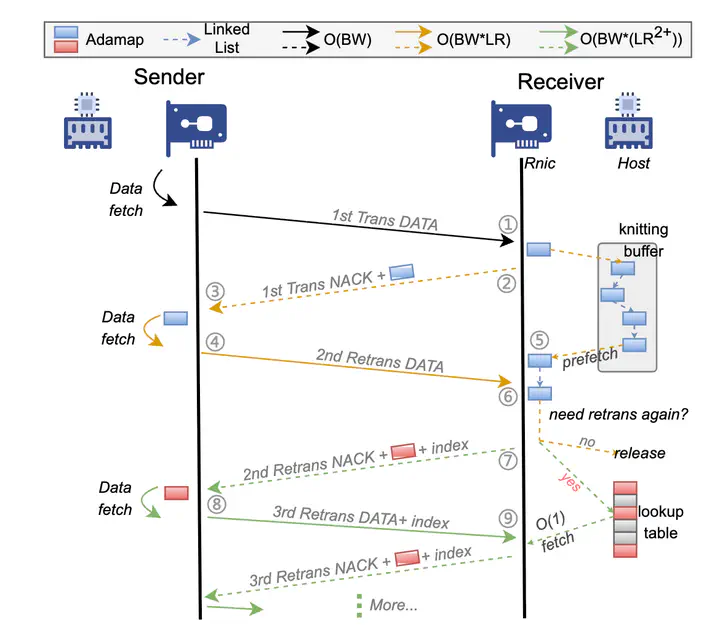
Modern cloud service providers and AI innovators are expanding their services across data centers to harness scale-out benefits while minimizing wide-area network (WAN) communication overhead. Although Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) has become the de-facto standard for high-speed data center networks, extending its benefits to WAN faces fundamental challenges: high bandwidth-delay products (BDP), frequent packet loss, and the inherent tension between performance and resource efficiency in existing approaches. To address these fundamental limitations and empower cross-datacenter services, we propose OmniDMA, a novel PFC-free RDMA architecture designed for loss-prone WAN environments. Our design introduces two core innovations: 1) The Adamap data structure enables flexible loss recording through context compression and management, and 2) a three-tier control path architecture that decouples retransmission from primary transmission control path, achieving high performance at WAN scale with minimal RNIC SRAM consumption. This design further reduces context management and scheduling overhead to guarantee line-rate processing under packet loss. Preliminary results demonstrate that OmniDMA achieves efficient RDMA communication over lossy WANs with constant resource consumption.